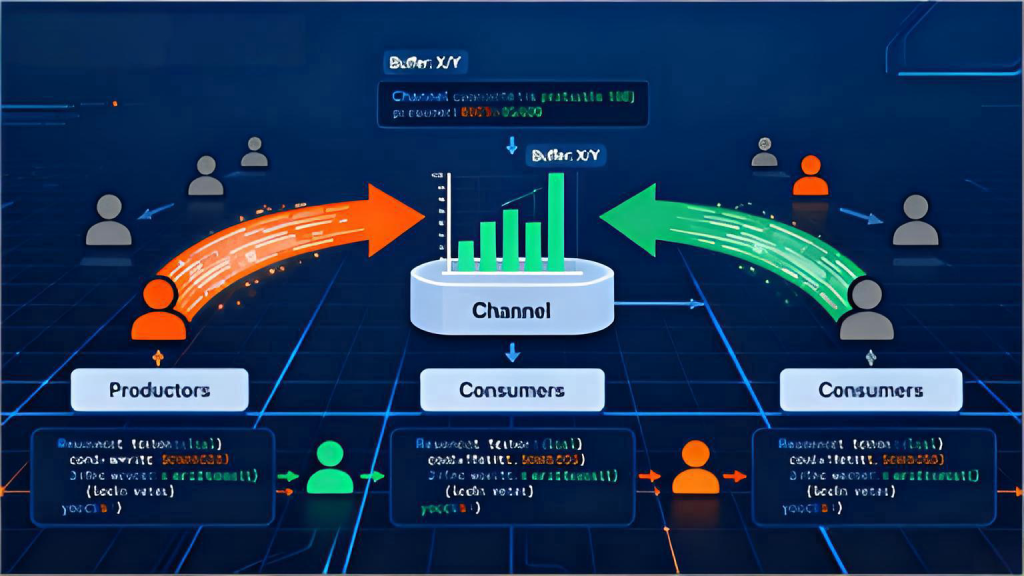
在现代C#应用程序开发中,处理高吞吐量的异步数据流是一个常见且具有挑战性的任务。传统的BlockingCollection和ConcurrentQueue虽然可用,但在异步场景下存在性能瓶颈和资源管理问题。System.Threading.Channel命名空间提供的Channel类型,为异步生产者消费者模式提供了全新的高性能解决方案。本文将深入解析Channel的实现原理和最佳实践。
![图片[1]-C#中Channel异步数据流处理:生产者消费者模式的高性能实现](https://blogimg.vcvcc.cc/2025/11/20251110132759441-1024x576.png?imageView2/0/format/webp/q/75)
一、问题现象:传统异步队列的性能瓶颈
1. 高并发下的性能衰减
典型场景:实时数据处理、消息队列消费者、日志批量处理等高频数据流场景。
性能症状:
- 内存分配率异常升高,GC压力增大
- 数据生产速度远大于消费速度时出现内存溢出
- 线程池线程大量消耗在同步等待上
- 吞吐量随并发数增加而达到平台期甚至下降
性能计数器异常:
Gen 0 Collections: 500+/sec
Thread Pool Threads: 100+
CPU Usage: 60%但吞吐量停滞2. 背压控制缺失导致的资源耗尽
错误现象:
System.OutOfMemoryException: Exception of type 'System.OutOfMemoryException' was thrown.
at System.Threading.Channels.Channel`1.CreateBounded[T](Int32 capacity, BoundedChannelFullMode fullMode)
at MyApp.DataProcessor.CreatePipeline()内存诊断显示:
- 未消费消息积压数:100,000+
- 生产者持续生产,消费者处理能力不足
- 缺乏有效的背压机制控制生产速度
3. 传统解决方案的局限性
BlockingCollection的问题代码:
// 传统BlockingCollection在异步场景的局限
public class TraditionalProducerConsumer
{
private readonly BlockingCollection<DataItem> _queue;
public TraditionalProducerConsumer(int boundedCapacity)
{
_queue = new BlockingCollection<DataItem>(boundedCapacity);
}
// 生产者 - 同步阻塞
public void Produce(DataItem item)
{
_queue.Add(item); // 可能阻塞生产者线程
}
// 消费者 - 异步转换复杂
public async Task StartConsumingAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
await Task.Run(() =>
{
foreach (var item in _queue.GetConsumingEnumerable())
{
ProcessItemAsync(item).Wait(); // 异步方法同步等待,可能死锁
}
});
}
private async Task ProcessItemAsync(DataItem item)
{
await Task.Delay(10); // 模拟异步处理
}
}二、Channel核心概念与架构解析
1. Channel类型体系与选择策略
Channel分类:
public class ChannelTypeExplorer
{
// 无界Channel - 内存风险但最高吞吐量
public static Channel<DataItem> CreateUnboundedChannel()
{
return Channel.CreateUnbounded<DataItem>(new UnboundedChannelOptions
{
// 单生产者单消费者优化
SingleReader = true,
SingleWriter = true,
// 允许同步continuations提升性能
AllowSynchronousContinuations = false
});
}
// 有界Channel - 背压控制但可能阻塞
public static Channel<DataItem> CreateBoundedChannel(int capacity)
{
return Channel.CreateBounded<DataItem>(new BoundedChannelOptions(capacity)
{
SingleReader = false,
SingleWriter = false,
AllowSynchronousContinuations = false,
// 满队列时的行为模式
FullMode = BoundedChannelFullMode.Wait
});
}
// 性能优化Channel配置
public static Channel<DataItem> CreateOptimizedChannel(int? capacity = null)
{
if (capacity.HasValue)
{
return Channel.CreateBounded<DataItem>(new BoundedChannelOptions(capacity.Value)
{
SingleReader = true, // 如果确实只有一个消费者
SingleWriter = false, // 通常有多个生产者
FullMode = BoundedChannelFullMode.Wait,
AllowSynchronousContinuations = true // 性能优化
});
}
else
{
return Channel.CreateUnbounded<DataItem>(new UnboundedChannelOptions
{
SingleReader = true,
SingleWriter = false,
AllowSynchronousContinuations = true
});
}
}
}2. Channel的读写接口语义
核心接口解析:
public class ChannelInterfaceDemo
{
public static async Task DemonstrateChannelApis()
{
var channel = Channel.CreateBounded<string>(10);
// 生产者接口
ChannelWriter<string> writer = channel.Writer;
// 写入方式1: TryWrite - 同步非阻塞
bool success = writer.TryWrite("item1");
// 写入方式2: WriteAsync - 异步可能等待
ValueTask writeTask = writer.WriteAsync("item2");
// 写入方式3: WaitToWriteAsync + TryWrite 模式
if (await writer.WaitToWriteAsync())
{
writer.TryWrite("item3");
}
// 完成写入
writer.Complete();
// 消费者接口
ChannelReader<string> reader = channel.Reader;
// 读取方式1: TryRead - 同步非阻塞
bool hasItem = reader.TryRead(out string item);
// 读取方式2: ReadAsync - 异步等待数据
string data = await reader.ReadAsync();
// 读取方式3: WaitToReadAsync + TryRead 模式
while (await reader.WaitToReadAsync())
{
while (reader.TryRead(out string nextItem))
{
ProcessItem(nextItem);
}
}
// 检查完成状态
await reader.Completion; // 等待Channel完全完成
}
private static void ProcessItem(string item)
{
// 处理逻辑
}
}三、高性能生产者消费者模式实现
1. 基础异步生产者消费者
完整实现方案:
public class AsyncChannelProcessor<T> : IAsyncDisposable
{
private readonly Channel<T> _channel;
private readonly ChannelWriter<T> _writer;
private readonly ChannelReader<T> _reader;
private readonly Func<T, CancellationToken, ValueTask> _processor;
private readonly CancellationTokenSource _cts;
private readonly Task _processingTask;
private readonly ILogger<AsyncChannelProcessor<T>> _logger;
private long _processedCount;
private bool _disposed = false;
public AsyncChannelProcessor(
int boundedCapacity,
Func<T, CancellationToken, ValueTask> processor,
ILogger<AsyncChannelProcessor<T>> logger,
bool singleReader = true)
{
_processor = processor;
_logger = logger;
_cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
// 创建有界Channel进行背压控制
var options = new BoundedChannelOptions(boundedCapacity)
{
SingleReader = singleReader,
SingleWriter = false,
FullMode = BoundedChannelFullMode.Wait,
AllowSynchronousContinuations = true
};
_channel = Channel.CreateBounded<T>(options);
_writer = _channel.Writer;
_reader = _channel.Reader;
// 启动后台处理任务
_processingTask = StartProcessingAsync(_cts.Token);
}
// 生产者接口 - 异步非阻塞
public async ValueTask<bool> ProduceAsync(T item, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
ObjectDisposedException.ThrowIf(_disposed, this);
try
{
await _writer.WriteAsync(item, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
return true;
}
catch (ChannelClosedException)
{
_logger.LogWarning("尝试向已关闭的Channel写入数据");
return false;
}
}
// 批量生产接口
public async ValueTask<int> ProduceBatchAsync(IEnumerable<T> items, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
ObjectDisposedException.ThrowIf(_disposed, this);
int count = 0;
foreach (var item in items)
{
if (cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
break;
try
{
await _writer.WriteAsync(item, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
count++;
}
catch (ChannelClosedException)
{
break;
}
}
return count;
}
// 消费者处理循环
private async Task StartProcessingAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Channel处理器启动");
try
{
await foreach (var item in _reader.ReadAllAsync(cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false))
{
try
{
await _processor(item, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
Interlocked.Increment(ref _processedCount);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException) when (cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
break;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "处理项目时发生错误: {Item}", item);
// 根据业务决定是否继续处理
}
}
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Channel处理器正常取消");
}
catch (ChannelClosedException)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Channel已关闭");
}
finally
{
_logger.LogInformation("Channel处理器停止,共处理 {Count} 个项目", _processedCount);
}
}
// 完成生产并等待处理完成
public async Task CompleteAsync(TimeSpan timeout = default)
{
ObjectDisposedException.ThrowIf(_disposed, this);
_writer.Complete();
var timeoutTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource(timeout);
try
{
await _processingTask.WaitAsync(timeoutTokenSource.Token).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
catch (TimeoutException)
{
_logger.LogWarning("Channel处理完成超时");
}
}
public long ProcessedCount => Interlocked.Read(ref _processedCount);
public async ValueTask DisposeAsync()
{
if (!_disposed)
{
_disposed = true;
// 取消处理
_cts.Cancel();
// 尝试优雅关闭
try
{
_writer.Complete();
await _processingTask.WaitAsync(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5)).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
catch (TimeoutException)
{
_logger.LogWarning("强制关闭Channel处理器");
}
finally
{
_cts.Dispose();
}
}
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
}2. 多消费者负载均衡模式
多消费者实现:
public class MultiConsumerChannelProcessor<T> : IAsyncDisposable
{
private readonly Channel<T> _channel;
private readonly ChannelWriter<T> _writer;
private readonly Task[] _consumerTasks;
private readonly CancellationTokenSource _cts;
private readonly ILogger<MultiConsumerChannelProcessor<T>> _logger;
private long _totalProcessed;
private bool _disposed = false;
public MultiConsumerChannelProcessor(
int boundedCapacity,
int consumerCount,
Func<T, CancellationToken, ValueTask> processor,
ILogger<MultiConsumerChannelProcessor<T>> logger)
{
if (consumerCount <= 0)
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(consumerCount));
_logger = logger;
_cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
// 多消费者场景,SingleReader必须为false
var options = new BoundedChannelOptions(boundedCapacity)
{
SingleReader = false,
SingleWriter = false,
FullMode = BoundedChannelFullMode.Wait,
AllowSynchronousContinuations = true
};
_channel = Channel.CreateBounded<T>(options);
_writer = _channel.Writer;
// 启动多个消费者
_consumerTasks = new Task[consumerCount];
for (int i = 0; i < consumerCount; i++)
{
int consumerId = i;
_consumerTasks[i] = StartConsumerAsync(consumerId, processor, _cts.Token);
}
_logger.LogInformation("启动 {ConsumerCount} 个消费者", consumerCount);
}
private async Task StartConsumerAsync(int consumerId, Func<T, CancellationToken, ValueTask> processor, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
_logger.LogInformation("消费者 {ConsumerId} 启动", consumerId);
try
{
await foreach (var item in _channel.Reader.ReadAllAsync(cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false))
{
try
{
await processor(item, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
Interlocked.Increment(ref _totalProcessed);
if (Interlocked.Read(ref _totalProcessed) % 1000 == 0)
{
_logger.LogDebug("消费者 {ConsumerId} 处理项目,总计: {Total}", consumerId, _totalProcessed);
}
}
catch (OperationCanceledException) when (cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
break;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "消费者 {ConsumerId} 处理项目时出错: {Item}", consumerId, item);
}
}
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
_logger.LogInformation("消费者 {ConsumerId} 正常取消", consumerId);
}
finally
{
_logger.LogInformation("消费者 {ConsumerId} 停止", consumerId);
}
}
public async ValueTask<bool> ProduceAsync(T item, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
ObjectDisposedException.ThrowIf(_disposed, this);
try
{
await _writer.WriteAsync(item, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
return true;
}
catch (ChannelClosedException)
{
return false;
}
}
public async Task CompleteAsync(TimeSpan timeout = default)
{
ObjectDisposedException.ThrowIf(_disposed, this);
_writer.Complete();
using var timeoutCts = new CancellationTokenSource(timeout);
try
{
await Task.WhenAll(_consumerTasks).WaitAsync(timeoutCts.Token).ConfigureAwait(false);
_logger.LogInformation("所有消费者完成,共处理 {Total} 个项目", _totalProcessed);
}
catch (TimeoutException)
{
_logger.LogWarning("消费者完成超时,已完成 {Total} 个项目", _totalProcessed);
}
}
public long TotalProcessed => Interlocked.Read(ref _totalProcessed);
public async ValueTask DisposeAsync()
{
if (!_disposed)
{
_disposed = true;
_cts.Cancel();
try
{
_writer.Complete();
await Task.WhenAll(_consumerTasks).WaitAsync(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5)).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
catch (TimeoutException)
{
_logger.LogWarning("强制关闭多消费者处理器");
}
finally
{
_cts.Dispose();
}
}
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
}3. 背压控制与速率限制
智能背压实现:
public class BackpressureChannelProcessor<T> : IAsyncDisposable
{
private readonly Channel<T> _channel;
private readonly ChannelWriter<T> _writer;
private readonly ChannelReader<T> _reader;
private readonly Func<T, CancellationToken, ValueTask> _processor;
private readonly CancellationTokenSource _cts;
private readonly Task _processingTask;
private readonly ILogger<BackpressureChannelProcessor<T>> _logger;
private readonly int _maxConcurrentOperations;
private readonly SemaphoreSlim _concurrencyLimiter;
private long _processedCount;
private long _backpressureEvents;
private bool _disposed = false;
public BackpressureChannelProcessor(
int channelCapacity,
int maxConcurrentOperations,
Func<T, CancellationToken, ValueTask> processor,
ILogger<BackpressureChannelProcessor<T>> logger)
{
_maxConcurrentOperations = maxConcurrentOperations;
_processor = processor;
_logger = logger;
_cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
_concurrencyLimiter = new SemaphoreSlim(maxConcurrentOperations);
var options = new BoundedChannelOptions(channelCapacity)
{
SingleReader = true,
SingleWriter = false,
FullMode = BoundedChannelFullMode.Wait
};
_channel = Channel.CreateBounded<T>(options);
_writer = _channel.Writer;
_reader = _channel.Reader;
_processingTask = StartProcessingWithBackpressureAsync(_cts.Token);
}
// 生产者接口,支持背压感知
public async ValueTask<ProductionResult> ProduceWithBackpressureAsync(
T item,
TimeSpan timeout,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
ObjectDisposedException.ThrowIf(_disposed, this);
using var timeoutCts = CancellationTokenSource.CreateLinkedTokenSource(cancellationToken);
timeoutCts.CancelAfter(timeout);
try
{
await _writer.WriteAsync(item, timeoutCts.Token).ConfigureAwait(false);
return ProductionResult.Success;
}
catch (OperationCanceledException) when (timeoutCts.Token.IsCancellationRequested)
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref _backpressureEvents);
return ProductionResult.Timeout;
}
catch (ChannelClosedException)
{
return ProductionResult.ChannelClosed;
}
}
// 带背压控制的处理循环
private async Task StartProcessingWithBackpressureAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
_logger.LogInformation("背压控制处理器启动,最大并发: {MaxConcurrent}", _maxConcurrentOperations);
try
{
await foreach (var item in _reader.ReadAllAsync(cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false))
{
// 获取并发许可,实现背压
await _concurrencyLimiter.WaitAsync(cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
// 启动后台处理,不阻塞读取循环
_ = ProcessItemWithLimiter(item, cancellationToken);
}
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
_logger.LogInformation("背压处理器正常取消");
}
finally
{
_logger.LogInformation("背压处理器停止");
}
}
private async Task ProcessItemWithLimiter(T item, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
try
{
await _processor(item, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
Interlocked.Increment(ref _processedCount);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException) when (cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
// 正常取消
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "处理项目时出错: {Item}", item);
}
finally
{
_concurrencyLimiter.Release();
}
}
// 背压状态监控
public BackpressureStatus GetBackpressureStatus()
{
int availablePermits = _concurrencyLimiter.CurrentCount;
int waitingProducers = _maxConcurrentOperations - availablePermits;
long backpressureCount = Interlocked.Read(ref _backpressureEvents);
return new BackpressureStatus
{
AvailablePermits = availablePermits,
WaitingProducers = waitingProducers,
TotalBackpressureEvents = backpressureCount,
ProcessedCount = Interlocked.Read(ref _processedCount),
IsHealthy = availablePermits > _maxConcurrentOperations * 0.2 // 20%余量
};
}
public async ValueTask DisposeAsync()
{
if (!_disposed)
{
_disposed = true;
_cts.Cancel();
try
{
_writer.Complete();
await _processingTask.WaitAsync(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10)).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
finally
{
_concurrencyLimiter.Dispose();
_cts.Dispose();
}
}
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
}
public enum ProductionResult
{
Success,
Timeout,
ChannelClosed
}
public class BackpressureStatus
{
public int AvailablePermits { get; set; }
public int WaitingProducers { get; set; }
public long TotalBackpressureEvents { get; set; }
public long ProcessedCount { get; set; }
public bool IsHealthy { get; set; }
}四、性能优化与监控策略
1. 性能基准测试对比
测试代码:
[MemoryDiagnoser]
[SimpleJob(RuntimeMoniker.Net60)]
public class ChannelPerformanceBenchmark
{
private const int ItemCount = 10000;
private readonly DataItem[] _testData;
public ChannelPerformanceBenchmark()
{
_testData = Enumerable.Range(0, ItemCount)
.Select(i => new DataItem { Id = i, Value = $"Value_{i}" })
.ToArray();
}
[Benchmark]
public async Task Channel_Unbounded_SingleConsumer()
{
var channel = Channel.CreateUnbounded<DataItem>();
var processor = new ChannelProcessor(channel, 1);
await ProduceDataAsync(channel.Writer);
await processor.CompleteAsync();
}
[Benchmark]
public async Task Channel_Bounded_MultiConsumer()
{
var channel = Channel.CreateBounded<DataItem>(1000);
var processor = new ChannelProcessor(channel, 4);
await ProduceDataAsync(channel.Writer);
await processor.CompleteAsync();
}
[Benchmark]
public async Task BlockingCollection_Traditional()
{
var collection = new BlockingCollection<DataItem>(1000);
var processor = new BlockingCollectionProcessor(collection, 4);
await ProduceDataAsync(collection);
await processor.CompleteAsync();
}
private async Task ProduceDataAsync(ChannelWriter<DataItem> writer)
{
foreach (var item in _testData)
{
await writer.WriteAsync(item);
}
writer.Complete();
}
private async Task ProduceDataAsync(BlockingCollection<DataItem> collection)
{
await Task.Run(() =>
{
foreach (var item in _testData)
{
collection.Add(item);
}
collection.CompleteAdding();
});
}
}
public class DataItem
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Value { get; set; }
}2. 实时性能监控
监控实现:
public class ChannelPerformanceMonitor
{
private readonly ILogger<ChannelPerformanceMonitor> _logger;
private readonly ConcurrentDictionary<string, ChannelMetrics> _metrics;
private readonly Timer _reportTimer;
public ChannelPerformanceMonitor(ILogger<ChannelPerformanceMonitor> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
_metrics = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, ChannelMetrics>();
_reportTimer = new Timer(ReportMetrics, null, TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1), TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1));
}
public void RecordProduction(string channelName, TimeSpan duration, bool success)
{
var metrics = _metrics.GetOrAdd(channelName, _ => new ChannelMetrics());
if (success)
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref metrics.ProducedCount);
metrics.RecordProductionTime(duration);
}
else
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref metrics.ProductionFailures);
}
}
public void RecordConsumption(string channelName, TimeSpan duration, bool success)
{
var metrics = _metrics.GetOrAdd(channelName, _ => new ChannelMetrics());
if (success)
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref metrics.ConsumedCount);
metrics.RecordConsumptionTime(duration);
}
else
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref metrics.ConsumptionFailures);
}
}
private void ReportMetrics(object state)
{
foreach (var (channelName, metrics) in _metrics)
{
var report = metrics.GenerateReport();
if (report.TotalThroughput > 0)
{
_logger.LogInformation(
"Channel {ChannelName} 性能报告: 生产 {Produced}/s, 消费 {Consumed}/s, 生产延迟 {ProdLatency}ms, 消费延迟 {ConsLatency}ms",
channelName,
report.ProductionThroughput,
report.ConsumptionThroughput,
report.AverageProductionLatencyMs,
report.AverageConsumptionLatencyMs);
}
metrics.ResetForNextPeriod();
}
}
public void Dispose()
{
_reportTimer?.Dispose();
}
}
public class ChannelMetrics
{
public long ProducedCount;
public long ConsumedCount;
public long ProductionFailures;
public long ConsumptionFailures;
private long _totalProductionTicks;
private long _totalConsumptionTicks;
private long _productionCount;
private long _consumptionCount;
public void RecordProductionTime(TimeSpan duration)
{
Interlocked.Add(ref _totalProductionTicks, duration.Ticks);
Interlocked.Increment(ref _productionCount);
}
public void RecordConsumptionTime(TimeSpan duration)
{
Interlocked.Add(ref _totalConsumptionTicks, duration.Ticks);
Interlocked.Increment(ref _consumptionCount);
}
public ChannelMetricsReport GenerateReport()
{
var productionCount = Interlocked.Read(ref _productionCount);
var consumptionCount = Interlocked.Read(ref _consumptionCount);
return new ChannelMetricsReport
{
ProducedCount = Interlocked.Read(ref ProducedCount),
ConsumedCount = Interlocked.Read(ref ConsumedCount),
ProductionFailures = Interlocked.Read(ref ProductionFailures),
ConsumptionFailures = Interlocked.Read(ref ConsumptionFailures),
AverageProductionLatencyMs = productionCount > 0 ?
TimeSpan.FromTicks(Interlocked.Read(ref _totalProductionTicks) / productionCount).TotalMilliseconds : 0,
AverageConsumptionLatencyMs = consumptionCount > 0 ?
TimeSpan.FromTicks(Interlocked.Read(ref _totalConsumptionTicks) / consumptionCount).TotalMilliseconds : 0,
ProductionThroughput = productionCount / 60.0, // 每分钟
ConsumptionThroughput = consumptionCount / 60.0,
TotalThroughput = (productionCount + consumptionCount) / 60.0
};
}
public void ResetForNextPeriod()
{
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _productionCount, 0);
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _consumptionCount, 0);
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _totalProductionTicks, 0);
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _totalConsumptionTicks, 0);
}
}
public class ChannelMetricsReport
{
public long ProducedCount { get; set; }
public long ConsumedCount { get; set; }
public long ProductionFailures { get; set; }
public long ConsumptionFailures { get; set; }
public double AverageProductionLatencyMs { get; set; }
public double AverageConsumptionLatencyMs { get; set; }
public double ProductionThroughput { get; set; }
public double ConsumptionThroughput { get; set; }
public double TotalThroughput { get; set; }
}五、实战应用场景与最佳实践
1. Web API请求处理管道
应用场景:
public class RequestProcessingPipeline
{
private readonly Channel<HttpContext> _requestChannel;
private readonly ChannelWriter<HttpContext> _writer;
private readonly ILogger<RequestProcessingPipeline> _logger;
private readonly CancellationTokenSource _cts;
private readonly Task[] _workerTasks;
private const int WorkerCount = 4;
public RequestProcessingPipeline(ILogger<RequestProcessingPipeline> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
_cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
// 创建有界Channel防止内存溢出
var options = new BoundedChannelOptions(1000)
{
SingleReader = false,
SingleWriter = false,
FullMode = BoundedChannelFullMode.Wait
};
_requestChannel = Channel.CreateBounded<HttpContext>(options);
_writer = _requestChannel.Writer;
// 启动工作线程
_workerTasks = new Task[WorkerCount];
for (int i = 0; i < WorkerCount; i++)
{
_workerTasks[i] = ProcessRequestsAsync(i, _cts.Token);
}
}
// MVC Filter或Middleware中调用
public async ValueTask<bool> EnqueueRequestAsync(HttpContext context, TimeSpan timeout)
{
using var timeoutCts = new CancellationTokenSource(timeout);
try
{
await _writer.WriteAsync(context, timeoutCts.Token).ConfigureAwait(false);
return true;
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
context.Response.StatusCode = 503; // Service Unavailable
return false;
}
}
private async Task ProcessRequestsAsync(int workerId, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
_logger.LogInformation("请求处理工作线程 {WorkerId} 启动", workerId);
await foreach (var context in _requestChannel.Reader.ReadAllAsync(cancellationToken))
{
try
{
await ProcessRequestAsync(context, cancellationToken);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "工作线程 {WorkerId} 处理请求时出错", workerId);
context.Response.StatusCode = 500;
}
}
_logger.LogInformation("请求处理工作线程 {WorkerId} 停止", workerId);
}
private async Task ProcessRequestAsync(HttpContext context, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
// 模拟请求处理
await Task.Delay(100, cancellationToken);
// 设置响应
context.Response.StatusCode = 200;
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Request processed", cancellationToken);
}
public async Task StopAsync()
{
_writer.Complete();
await Task.WhenAll(_workerTasks).WaitAsync(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30));
_cts.Dispose();
}
}2. 数据库批量写入优化
批量处理场景:
public class BatchDatabaseWriter<T> : IAsyncDisposable
{
private readonly Channel<T> _channel;
private readonly ChannelWriter<T> _writer;
private readonly Task _batchWriterTask;
private readonly CancellationTokenSource _cts;
private readonly Func<List<T>, CancellationToken, Task> _batchInsert;
private readonly int _batchSize;
private readonly TimeSpan _batchTimeout;
private readonly ILogger<BatchDatabaseWriter<T>> _logger;
private bool _disposed = false;
public BatchDatabaseWriter(
int channelCapacity,
int batchSize,
TimeSpan batchTimeout,
Func<List<T>, CancellationToken, Task> batchInsert,
ILogger<BatchDatabaseWriter<T>> logger)
{
_batchSize = batchSize;
_batchTimeout = batchTimeout;
_batchInsert = batchInsert;
_logger = logger;
_cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
var options = new BoundedChannelOptions(channelCapacity)
{
SingleReader = true,
SingleWriter = false,
FullMode = BoundedChannelFullMode.Wait
};
_channel = Channel.CreateBounded<T>(options);
_writer = _channel.Writer;
_batchWriterTask = StartBatchWritingAsync(_cts.Token);
}
public async ValueTask<bool> WriteAsync(T item, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
ObjectDisposedException.ThrowIf(_disposed, this);
try
{
await _writer.WriteAsync(item, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
return true;
}
catch (ChannelClosedException)
{
return false;
}
}
private async Task StartBatchWritingAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var batch = new List<T>(_batchSize);
var batchTimer = new PeriodicTimer(_batchTimeout);
try
{
while (await _channel.Reader.WaitToReadAsync(cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false))
{
// 收集批次或超时
while (batch.Count < _batchSize &&
await batchTimer.WaitForNextTickAsync(cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false))
{
while (batch.Count < _batchSize && _channel.Reader.TryRead(out var item))
{
batch.Add(item);
}
if (batch.Count > 0)
{
await FlushBatchAsync(batch, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
batch.Clear();
}
}
}
// 处理剩余数据
if (batch.Count > 0)
{
await FlushBatchAsync(batch, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
_logger.LogInformation("批量写入器正常取消");
}
finally
{
batchTimer.Dispose();
}
}
private async Task FlushBatchAsync(List<T> batch, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
try
{
await _batchInsert(batch, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
_logger.LogDebug("成功写入 {Count} 个项目", batch.Count);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "批量写入失败: {Count} 个项目", batch.Count);
// 根据业务需求决定重试策略
}
}
public async ValueTask DisposeAsync()
{
if (!_disposed)
{
_disposed = true;
_writer.Complete();
_cts.Cancel();
try
{
await _batchWriterTask.WaitAsync(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30)).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
catch (TimeoutException)
{
_logger.LogWarning("批量写入器关闭超时");
}
finally
{
_cts.Dispose();
}
}
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
}总结
C# Channel为异步生产者消费者模式提供了高性能、内存安全的解决方案。通过本文的深入分析和实践,我们可以得出以下关键要点:
- 正确选择Channel类型:根据场景选择有界或无界Channel,平衡吞吐量与内存使用
- 合理配置Channel选项:利用SingleReader/SingleWriter优化性能,合理设置FullMode处理背压
- 实现健壮的背压控制:通过有界Channel和并发限制防止系统过载
- 监控与诊断:建立完善的性能监控体系,实时掌握Channel运行状态
- 优雅关闭机制:确保在应用程序关闭时正确处理剩余数据和资源释放
Channel的合理使用能够显著提升高并发场景下的数据处理能力,是现代C#异步编程不可或缺的重要工具。
© 版权声明
THE END












暂无评论内容